Page 85 - NETWORK ANALYSIS
P. 85
77
Norton Theorem
By using Ohms Law,
V (100)
IN = R T = (10 − j10) = (5 + j5) A
Step 3
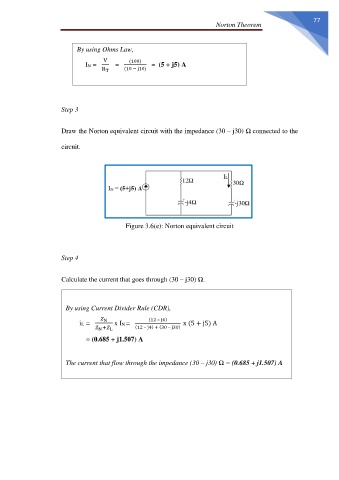
Draw the Norton equivalent circuit with the impedance (30 – j30) Ω connected to the
circuit.
Figure 3.6(e): Norton equivalent circuit
Step 4
Calculate the current that goes through (30 – j30) Ω.
By using Current Divider Rule (CDR),
N (12 – j4)
iL = x IN = x (5 + j5) A
+ L (12 – j4) + (30 – j30)
N
= (0.685 + j1.507) A
The current that flow through the impedance (30 – j30) Ω = (0.685 + j1.507) A