Page 22 - BASIC CONCEPTUAL OF THERMOFLUID
P. 22
CHAPTER 2: FLUID APPLICATION
Example 2.4
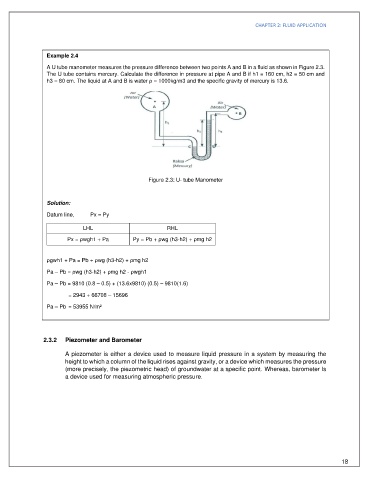
A U tube manometer measures the pressure difference between two points A and B in a fluid as shown in Figure 2.3.
The U tube contains mercury. Calculate the difference in pressure at pipe A and B if h1 = 160 cm, h2 = 50 cm and
h3 = 80 cm. The liquid at A and B is water ρ = 1000kg/m3 and the specific gravity of mercury is 13.6.
Figure 2.3: U- tube Manometer
Solution:
Datum line, Px = Py
LHL RHL
Px = ρwgh1 + Pa Py = Pb + ρwg (h3-h2) + ρmg h2
ρgwh1 + Pa = Pb + ρwg (h3-h2) + ρmg h2
Pa – Pb = ρwg (h3-h2) + ρmg h2 - ρwgh1
Pa – Pb = 9810 (0.8 – 0.5) + (13.6x9810) (0.5) – 9810(1.6)
= 2943 + 66708 – 15696
Pa – Pb = 53955 N/m²
2.3.2 Piezometer and Barometer
A piezometer is either a device used to measure liquid pressure in a system by measuring the
height to which a column of the liquid rises against gravity, or a device which measures the pressure
(more precisely, the piezometric head) of groundwater at a specific point. Whereas, barometer Is
a device used for measuring atmospheric pressure.
18