Page 20 - POLYMER TECHNOLOGY
P. 20
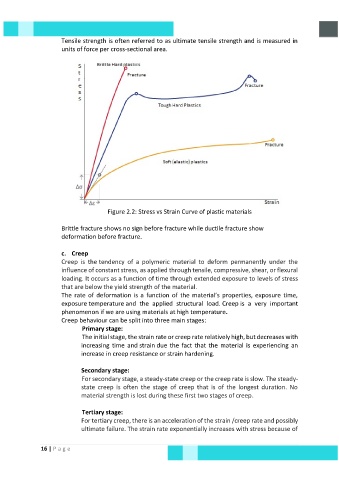
Tensile strength is often referred to as ultimate tensile strength and is measured in
units of force per cross-sectional area.
Figure 2.2: Stress vs Strain Curve of plastic materials
Brittle fracture shows no sign before fracture while ductile fracture show
deformation before fracture.
c. Creep
Creep is the tendency of a polymeric material to deform permanently under the
influence of constant stress, as applied through tensile, compressive, shear, or flexural
loading. It occurs as a function of time through extended exposure to levels of stress
that are below the yield strength of the material.
The rate of deformation is a function of the material’s properties, exposure time,
exposure temperature and the applied structural load. Creep is a very important
phenomenon if we are using materials at high temperature.
Creep behaviour can be split into three main stages:
Primary stage:
The initial stage, the strain rate or creep rate relatively high, but decreases with
increasing time and strain due the fact that the material is experiencing an
increase in creep resistance or strain hardening.
Secondary stage:
For secondary stage, a steady-state creep or the creep rate is slow. The steady-
state creep is often the stage of creep that is of the longest duration. No
material strength is lost during these first two stages of creep.
Tertiary stage:
For tertiary creep, there is an acceleration of the strain /creep rate and possibly
ultimate failure. The strain rate exponentially increases with stress because of
16 | P a g e