Page 15 - POLYMER TECHNOLOGY
P. 15
b. Condensation Polymerization (Step Growth Polymerization)
A condensation polymerization is a form of step-growth polymerization in which
monomers react with each other to form larger structural units while releasing smaller
molecules as a by-product such as water. The monomers for condensation
polymerization have two main characteristics, instead of double bonds, these
monomers have functional groups (like alcohol, amine, or carboxylic acid groups) and
each monomer has at least two reactive sites, which usually means two functional
groups. Some monomers have more than two reactive sites, allowing for branching
between chains, as well as increasing the molecular mass of the polymer.
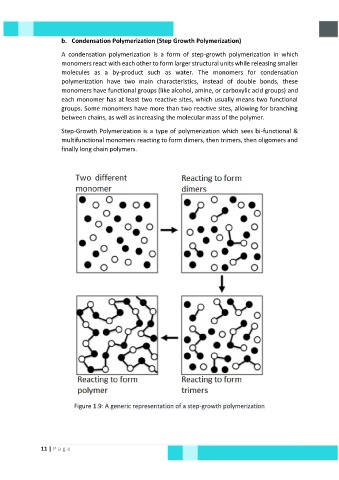
Step-Growth Polymerization is a type of polymerization which sees bi-functional &
multifunctional monomers reacting to form dimers, then trimers, then oligomers and
finally long chain polymers.
Figure 1.9: A generic representation of a step-growth polymerization
11 | P a g e