Page 11 - POLYMER TECHNOLOGY
P. 11
1.5 Molecules generated by repeating monomer unit.
Polymers are macromolecule of recurring monomer units. The monomers are
connected to each other according to the types of polymer chain structures. The
process of combination monomers into polymers is known as the polymerization
process.
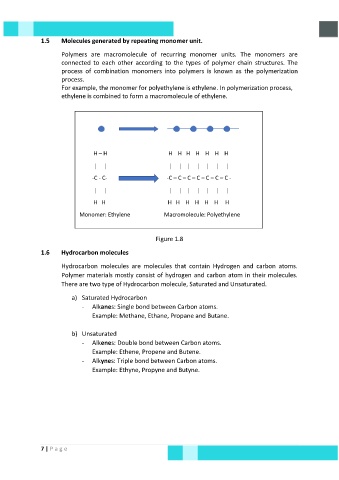
For example, the monomer for polyethylene is ethylene. In polymerization process,
ethylene is combined to form a macromolecule of ethylene.
H – H H H H H H H H
-C - C- -C – C – C – C – C – C – C -
H H H H H H H H H
Monomer: Ethylene Macromolecule: Polyethylene
Figure 1.8
1.6 Hydrocarbon molecules
Hydrocarbon molecules are molecules that contain Hydrogen and carbon atoms.
Polymer materials mostly consist of hydrogen and carbon atom in their molecules.
There are two type of Hydrocarbon molecule, Saturated and Unsaturated.
a) Saturated Hydrocarbon
- Alkanes: Single bond between Carbon atoms.
Example: Methane, Ethane, Propane and Butane.
b) Unsaturated
- Alkenes: Double bond between Carbon atoms.
Example: Ethene, Propene and Butene.
- Alkynes: Triple bond between Carbon atoms.
Example: Ethyne, Propyne and Butyne.
7 | P a g e