Page 19 - POLYMER TECHNOLOGY
P. 19
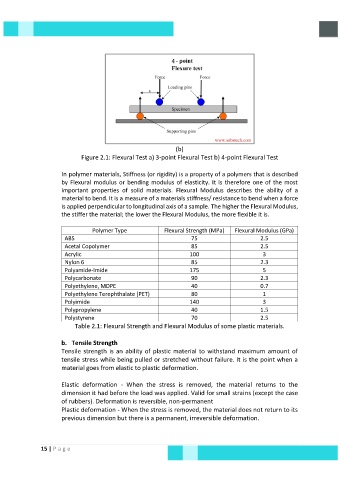
(b)
Figure 2.1: Flexural Test a) 3-point Flexural Test b) 4-point Flexural Test
In polymer materials, Stiffness (or rigidity) is a property of a polymers that is described
by Flexural modulus or bending modulus of elasticity. It is therefore one of the most
important properties of solid materials. Flexural Modulus describes the ability of a
material to bend. It is a measure of a materials stiffness/ resistance to bend when a force
is applied perpendicular to longitudinal axis of a sample. The higher the Flexural Modulus,
the stiffer the material; the lower the Flexural Modulus, the more flexible it is.
Polymer Type Flexural Strength (MPa) Flexural Modulus (GPa)
ABS 75 2.5
Acetal Copolymer 85 2.5
Acrylic 100 3
Nylon 6 85 2.3
Polyamide-Imide 175 5
Polycarbonate 90 2.3
Polyethylene, MDPE 40 0.7
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) 80 1
Polyimide 140 3
Polypropylene 40 1.5
Polystyrene 70 2.5
Table 2.1: Flexural Strength and Flexural Modulus of some plastic materials.
b. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength is an ability of plastic material to withstand maximum amount of
tensile stress while being pulled or stretched without failure. It is the point when a
material goes from elastic to plastic deformation.
Elastic deformation - When the stress is removed, the material returns to the
dimension it had before the load was applied. Valid for small strains (except the case
of rubbers). Deformation is reversible, non-permanent
Plastic deformation - When the stress is removed, the material does not return to its
previous dimension but there is a permanent, irreversible deformation.
15 | P a g e