Page 13 - BASIC CONCEPTUAL OF THERMOFLUID
P. 13
CHAPTER 1: CONCEPTUAL PRINCIPLE IN THERMOFLUIDS
Any thermodynamic system must meet the above equilibrium state to be considered as system in
the state of thermodynamic equilibrium. A thermodynamic system will be considered in the state
of non-equilibrium, if system is not meeting anyone above equilibrium state.
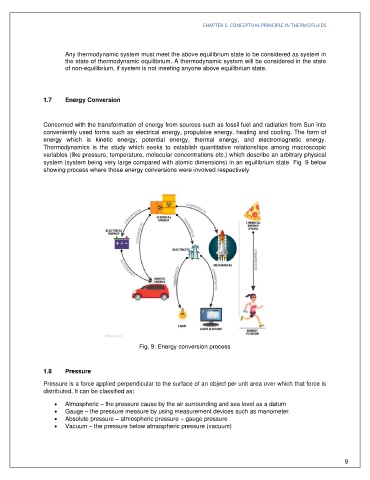
1.7 Energy Conversion
Concerned with the transformation of energy from sources such as fossil fuel and radiation from Sun into
conveniently used forms such as electrical energy, propulsive energy, heating and cooling. The form of
energy which is kinetic energy, potential energy, thermal energy, and electromagnetic energy.
Thermodynamics is the study which seeks to establish quantitative relationships among macroscopic
variables (like pressure, temperature, molecular concentrations etc.) which describe an arbitrary physical
system (system being very large compared with atomic dimensions) in an equilibrium state. Fig. 9 below
showing process where those energy conversions were involved respectively.
Fig. 9: Energy conversion process
1.8 Pressure
Pressure is a force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is
distributed. It can be classified as:
• Atmospheric – the pressure cause by the air surrounding and sea level as a datum
• Gauge – the pressure measure by using measurement devices such as manometer.
• Absolute pressure – atmospheric pressure + gauge pressure
• Vacuum – the pressure below atmospheric pressure (vacuum)
9