Page 33 - POLYMER TECHNOLOGY
P. 33
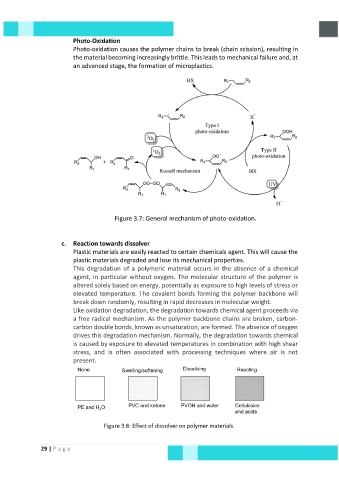
Photo-Oxidation
Photo-oxidation causes the polymer chains to break (chain scission), resulting in
the material becoming increasingly brittle. This leads to mechanical failure and, at
an advanced stage, the formation of microplastics.
Figure 3.7: General mechanism of photo-oxidation.
c. Reaction towards dissolver
Plastic materials are easily reacted to certain chemicals agent. This will cause the
plastic materials degraded and lose its mechanical properties.
This degradation of a polymeric material occurs in the absence of a chemical
agent, in particular without oxygen. The molecular structure of the polymer is
altered solely based on energy, potentially as exposure to high levels of stress or
elevated temperature. The covalent bonds forming the polymer backbone will
break down randomly, resulting in rapid decreases in molecular weight.
Like oxidation degradation, the degradation towards chemical agent proceeds via
a free radical mechanism. As the polymer backbone chains are broken, carbon-
carbon double bonds, known as unsaturation, are formed. The absence of oxygen
drives this degradation mechanism. Normally, the degradation towards chemical
is caused by exposure to elevated temperatures in combination with high shear
stress, and is often associated with processing techniques where air is not
present.
Figure 3.8: Effect of dissolver on polymer materials.
29 | P a g e