Page 29 - POLYMER TECHNOLOGY
P. 29
material are an importance and being used in product design, engineering, and
product manufacturing, making the heat distortion temperature testing of plastics
important.
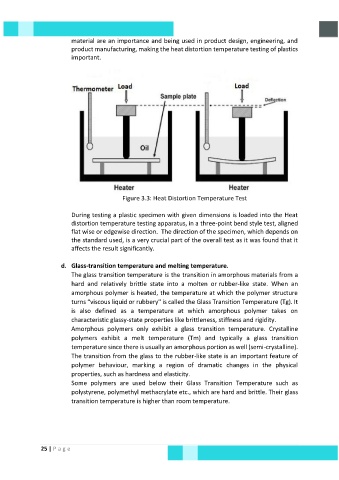
Figure 3.3: Heat Distortion Temperature Test
During testing a plastic specimen with given dimensions is loaded into the Heat
distortion temperature testing apparatus, in a three-point bend style test, aligned
flat wise or edgewise direction. The direction of the specimen, which depends on
the standard used, is a very crucial part of the overall test as it was found that it
affects the result significantly.
d. Glass-transition temperature and melting temperature.
The glass transition temperature is the transition in amorphous materials from a
hard and relatively brittle state into a molten or rubber-like state. When an
amorphous polymer is heated, the temperature at which the polymer structure
turns “viscous liquid or rubbery" is called the Glass Transition Temperature (Tg). It
is also defined as a temperature at which amorphous polymer takes on
characteristic glassy-state properties like brittleness, stiffness and rigidity.
Amorphous polymers only exhibit a glass transition temperature. Crystalline
polymers exhibit a melt temperature (Tm) and typically a glass transition
temperature since there is usually an amorphous portion as well (semi-crystalline).
The transition from the glass to the rubber-like state is an important feature of
polymer behaviour, marking a region of dramatic changes in the physical
properties, such as hardness and elasticity.
Some polymers are used below their Glass Transition Temperature such as
polystyrene, polymethyl methacrylate etc., which are hard and brittle. Their glass
transition temperature is higher than room temperature.
25 | P a g e