Page 56 - BASIC CONCEPTUAL OF THERMOFLUID
P. 56
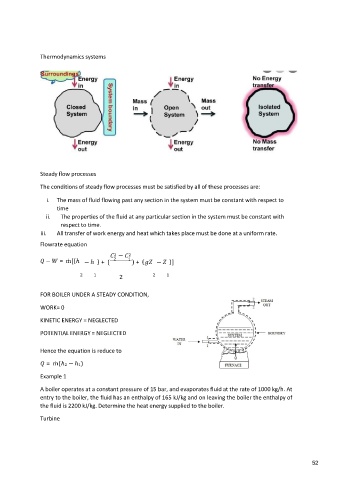
Thermodynamics systems
Steady flow processes
The conditions of steady flow processes must be satisfied by all of these processes are:
i. The mass of fluid flowing past any section in the system must be constant with respect to
time
ii. The properties of the fluid at any particular section in the system must be constant with
respect to time.
iii. All transfer of work energy and heat which takes place must be done at a uniform rate.
Flowrate equation
ܥ − ܥ 2
2
ܳ − ܹ = ṁ[(ℎ − ℎ ) + ( 2 1 ) + (ܼ݃ − ܼ )]
2 1 2 1
2
FOR BOILER UNDER A STEADY CONDITION,
WORK= 0
KINETIC ENERGY = NEGLECTED
POTENTIAL ENERGY = NEGLECTED
Hence the equation is reduce to
ܳ = ṁ(ℎ2 − ℎ1)
Example 1
A boiler operates at a constant pressure of 15 bar, and evaporates fluid at the rate of 1000 kg/h. At
entry to the boiler, the fluid has an enthalpy of 165 kJ/kg and on leaving the boiler the enthalpy of
the fluid is 2200 kJ/kg. Determine the heat energy supplied to the boiler.
Turbine
52