Page 27 - SATELLITE AND RADAR COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
P. 27
Footprint Categories
The Spot and Zonal Beams:
– Concentrated power to very small geographical areas
– Have high EIRPs
– Blanket less than 10% of earth’s surface
Hemispherical Beam
– Blanket 20% of Earth’s surface
– Have EIRP that are 3dB lower than spot beams
Earth (Global)
– Beam width of approximately 17˚
– Coverage of up to 42% of earth’s surface
– Power levels are considerably low
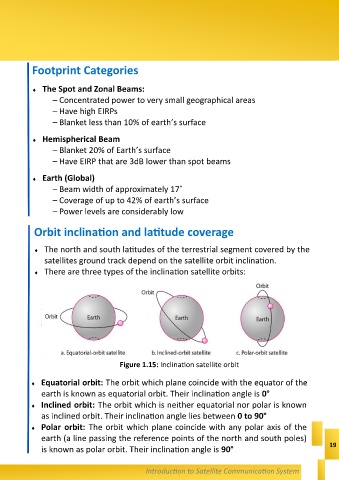
Orbit inclination and latitude coverage
The north and south latitudes of the terrestrial segment covered by the
satellites ground track depend on the satellite orbit inclination.
There are three types of the inclination satellite orbits:
Figure 1.15: Inclination satellite orbit
Equatorial orbit: The orbit which plane coincide with the equator of the
earth is known as equatorial orbit. Their inclination angle is 0°
Inclined orbit: The orbit which is neither equatorial nor polar is known
as inclined orbit. Their inclination angle lies between 0 to 90°
Polar orbit: The orbit which plane coincide with any polar axis of the
earth (a line passing the reference points of the north and south poles)
19
is known as polar orbit. Their inclination angle is 90°
Introduction to Satellite Communication System