Page 50 - PNEUMATIC SYSTEM INSTRUMENT
P. 50
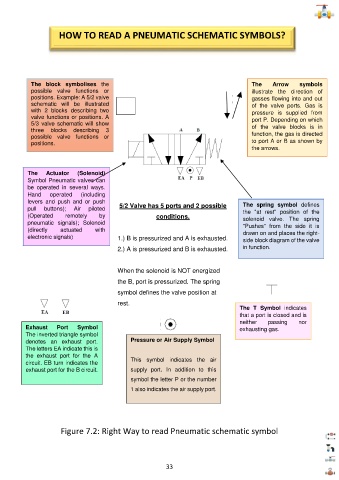
HOW TO READ A PNEUMATIC SCHEMATIC SYMBOLS?
The block symbolises the The Arrow symbols
possible valve functions or illustrate the direction of
posit ions. Example: A 5/2 valve gasses flowing into and out
schematic will be illustrated of the valve ports. Gas is
with 2 blocks describing two pressure is supplied from
valve functions or positions. A port P. Depending on which
5/3 valve schematic will show of the valve blocks is in
three blocks describing 3
possible valve functions or function, the gas is directed
positions. to port A or B as shown by
the arrows.
The Actuator (Solenoid)
Symbol Pneumatic valves can
be operated in several ways.
Hand operated (including
levers and push and or push The spring symbol defines
pull buttons); Air piloted 5/2 Valve has 5 ports and 2 possible the "at rest" position of the
(Operated remotely by conditions. solenoid valve. The spring
pneumatic signals); Solenoid "Pushes" from the side it is
(directly actuated with drawn on and places the right-
electronic signals) 1.) B is pressurized and A is exhausted. side block diagram of the valve
2.) A is pressurized and B is exhausted. in function.
When the solenoid is NOT energized
the B, port is pressurized. The spring
symbol defines the valve position at
rest.
The T Symbol indicates
that a port is closed and is
neither passing nor
Exhaust Port Symbol exhausting gas.
The inverted triangle symbol
denotes an exhaust port. Pressure or Air Supply Symbol
The letters EA indicate this is
the exhaust port for the A
circuit. EB turn indicates the This symbol indicates the air
exhaust port for the B circuit. supply port. In addition to this
symbol the letter P or the number
1 also indicates the air supply port.
Figure 7.2: Right Way to read Pneumatic schematic symbol
33