Page 15 - SATELLITE AND RADAR COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
P. 15
1.2 Understand frequency
allocations for satellite
communication system
Frequency band allocations for
satellite communication
system
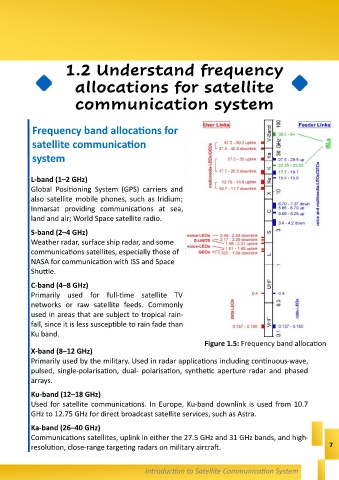
L-band (1–2 GHz)
Global Positioning System (GPS) carriers and
also satellite mobile phones, such as Iridium;
Inmarsat providing communications at sea,
land and air; World Space satellite radio.
S-band (2–4 GHz)
Weather radar, surface ship radar, and some
communications satellites, especially those of
NASA for communication with ISS and Space
Shuttle.
C-band (4–8 GHz)
Primarily used for full-time satellite TV
networks or raw satellite feeds. Commonly
used in areas that are subject to tropical rain-
fall, since it is less susceptible to rain fade than
Ku band.
Figure 1.5: Frequency band allocation
X-band (8–12 GHz)
Primarily used by the military. Used in radar applications including continuous-wave,
pulsed, single-polarisation, dual- polarisation, synthetic aperture radar and phased
arrays.
Ku-band (12–18 GHz)
Used for satellite communications. In Europe, Ku-band downlink is used from 10.7
GHz to 12.75 GHz for direct broadcast satellite services, such as Astra.
Ka-band (26–40 GHz)
Communications satellites, uplink in either the 27.5 GHz and 31 GHz bands, and high-
resolution, close-range targeting radars on military aircraft. 7
Introduction to Satellite Communication System